

Esmaeel Alshikh - 5 min read
Understanding Voltage Systems: Definitions and Basic Principles
Common Applications of 12V, 24V, and 48V Systems
Pros and Cons of Each Voltage System
Comparing 12V, 24V, and 48V Systems
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Voltage System
Expert Insights and Recommendations
Actionable Tips for Selecting the Right Voltage
Conclusion
Choosing the right voltage for your power system can feel like searching for a needle in a haystack. It’s a vital choice that affects safety, costs, and the overall performance of your setup. Whether you’re putting in solar panels, equipping an RV, or establishing an industrial system, knowing the differences between 12V, 24V, and 48V can empower you to make better decisions. Let’s dive into what each voltage level brings to the table and figure out what might work best
for you.

Voltage is essentially the electrical pressure that drives current through wires. You can think of it like the water pressure in a hose. The higher the voltage, the more power can travel over long distances and support
heavier loads. But keep in mind, with higher voltage comes greater safety risks if it’s not managed properly.

Voltage Level | Advantages | Disadvantages |
12V | Cheap, widely available, safe | Less efficient, thicker wires needed |
24V | Better efficiency, fewer wires | Slightly more complex, higher cost |
48V | Highly efficient, supports large loads | Higher safety risks, more expensive components |
Higher voltage levels mean less energy is wasted as heat. Consider 48V systems; they greatly reduce power loss across great distances. Data shows systems running above 24V can cut energy waste by as much as 50 percent. Thus, choosing a higher voltage, like 48V, can help you save money and improve performance if you’re building up a big system or handling long cables.
Voltage | Best Use Case | Current Load | Efficiency | Expandability |
12V | Small and mobile setups | High | Low | Very Limited |
24V | Medium homes or small business | Moderate | Good | Excellent |
48V | Large homes, farms, industrial | Low | Excellent | Excellent |
The least expensive and easiest to install are 12V systems. The parts are widely accessible. However, the requirement for larger batteries and thicker wires may result in more expenses for larger systems. Conversely, 48V systems are more costly at first but save money over time due to their increased efficiency and lower wiring requirements.
Usually safe to operate with are lower voltage systems like 12V. Minimal risk of major shock exists even in exposed wires.
By contrast, 48V systems increase risk and need appropriate insulation, grounding, and trained handling to guarantee safety.
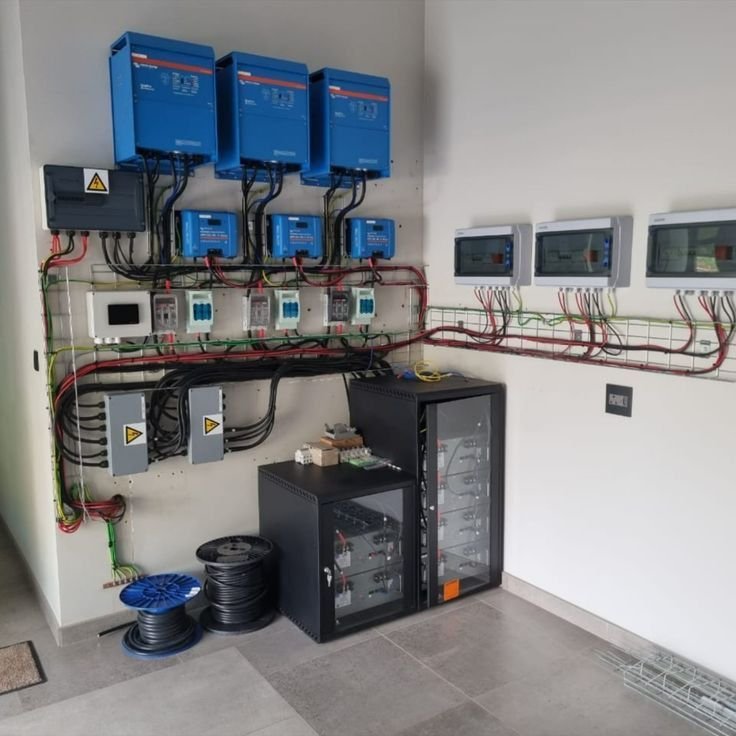

Small projects like cars or tiny houses fit 12V systems rather nicely.
A 24V or 48V system lets you quickly expand if your expected energy demand is rising. These systems allow for more adaptability in adding later on solar panels or new appliances.
Systems with higher voltages use less energy, which lessens their impact on the environment and energy waste. 48V systems are a wise, environmentally friendly choice if you want to lessen your carbon footprint.
Engineers usually advise 12V or 24V for small-scale and mobile systems due to convenience and safety.
48V is more scalable and effective for large-scale or permanent systems, particularly solar-powered ones.
Higher voltage systems are becoming more popular because of their long-term performance and energy savings.Best safaris in Africa
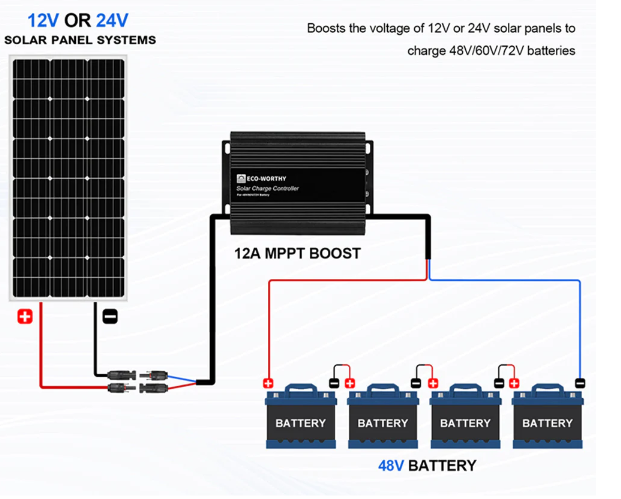
Depending on your particular circumstances, you can choose between 12V, 24V, and 48V.
For compact, portable setups, 12V is perfect. Also, mid-size systems, 24V, provide a good balance, and large, long-term systems where efficiency and performance are crucial, 48V stands out.
Carefully consider your energy requirements, financial constraints, available space, and potential growth requirements. Your power setup will continue to be safe, scalable, and effective for many years with a carefully chosen voltage system.